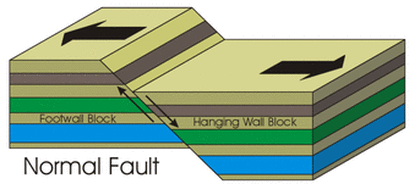
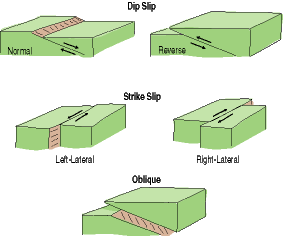
Normal if a fault is nearly vertical in orientation and the two walls of rock on opposite sides slide past one another horizontally the fault is termed.
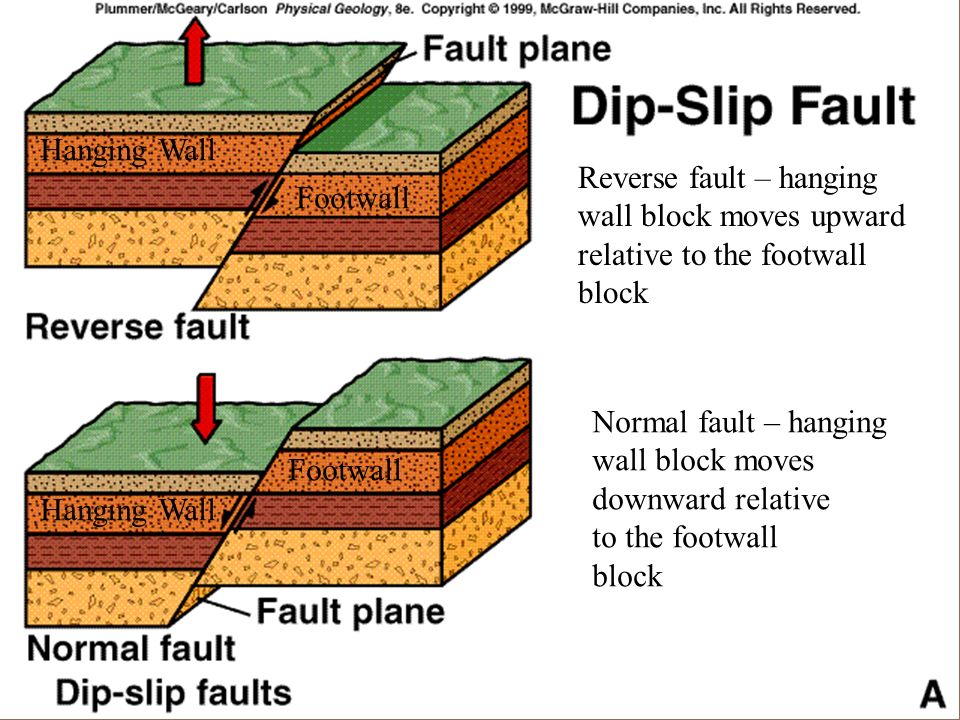
If during an earthquake a hanging wall slides downward relative to a footwall.
If during an earthquake a football slides upwards relative to a hanging wall the fault is termed a normal if a fault is nearly vertical in orientation and the two walls of rocks on opposite sides slide past one another horizontally the fault is termed.
Get more help from chegg get 1 1 help now from expert earth sciences tutors.
Refer to the figure below for an example of such a feature.
Transcribed image text if during an earthquake a hanging wall slides upward relative to a footwall the fault is termed only if the fault has a gradient less than 30 degrees closer to horizontal than vertical.
During an earthquake if a hanging wall slides upward relative to a footwall the fault is termed a fault if the fault is shallow much closer to horizontal than vertical.
If during an earthquake a hanging wall slides upward relative to a footwall the fault is termed if the fault is steep closer to vertical than horizontal.
During an earthquake if the hanging wall slides upward relative to the footwall the fault is termed a fault if the fault is steep closer to vertical than horizontal.
Refer to the figure below for an example of such a feature.
If during an earthquake a hanging wall slides upward relative to a footwall the fault is termed if the fault is shallow much closer to horizontal than vertical.